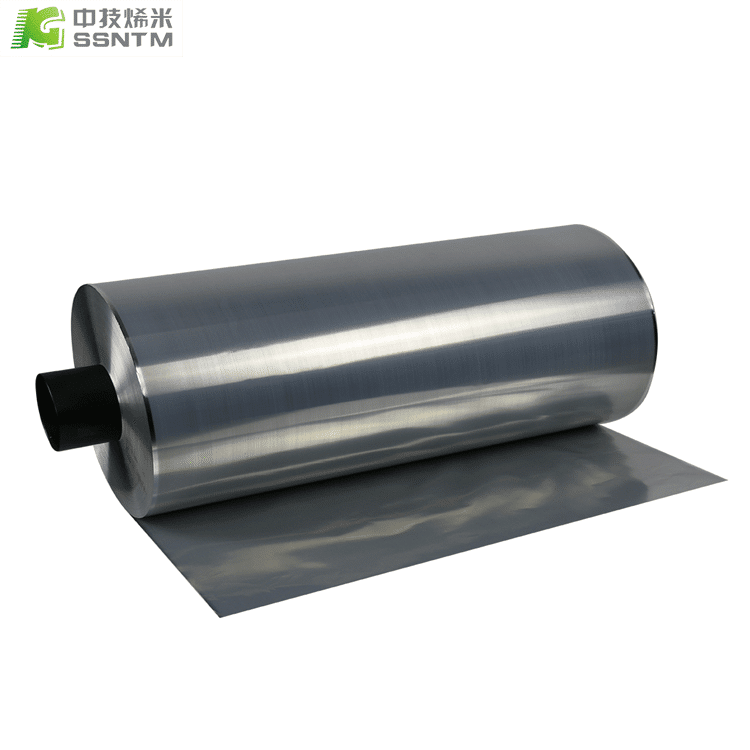
Copper is commonly used as a current collector in batteries due to its high electrical conductivity, low resistance, and good corrosion resistance.
Copper has a high electrical conductivity, meaning that it can efficiently transfer electrons generated by the electrochemical reaction in a battery to the external circuit. It has a low resistance which in turn reduces energy losses during electron transfer.

Furthermore, copper’s good corrosion resistance makes it less susceptible to degradation from the chemical environment inside most batteries. This ensures that the current collector maintains its electrical conductivity and mechanical integrity during the battery’s lifetime.
Finally, copper is widely available and cost-effective compared to other high conductivity materials such as silver or gold, making it a practical choice for current collectors in large-scale battery production.
As a result, copper is a popular choice for current collectors in a wide range of battery applications, including many commercial lithium-ion batteries.