What is a lithium-ion battery?
Lithium ion batteries are a type of secondary battery (rechargeable battery) that primarily relies on the movement of lithium ions between the positive and negative electrodes for operation. During the charging and discharging process, Li+is intercalated and disembedded back and forth between the two electrodes: during charging, Li+is disembedded from the positive electrode, embedded into the negative electrode through the electrolyte, and the negative electrode is in a lithium rich state; When discharging, the opposite is true.
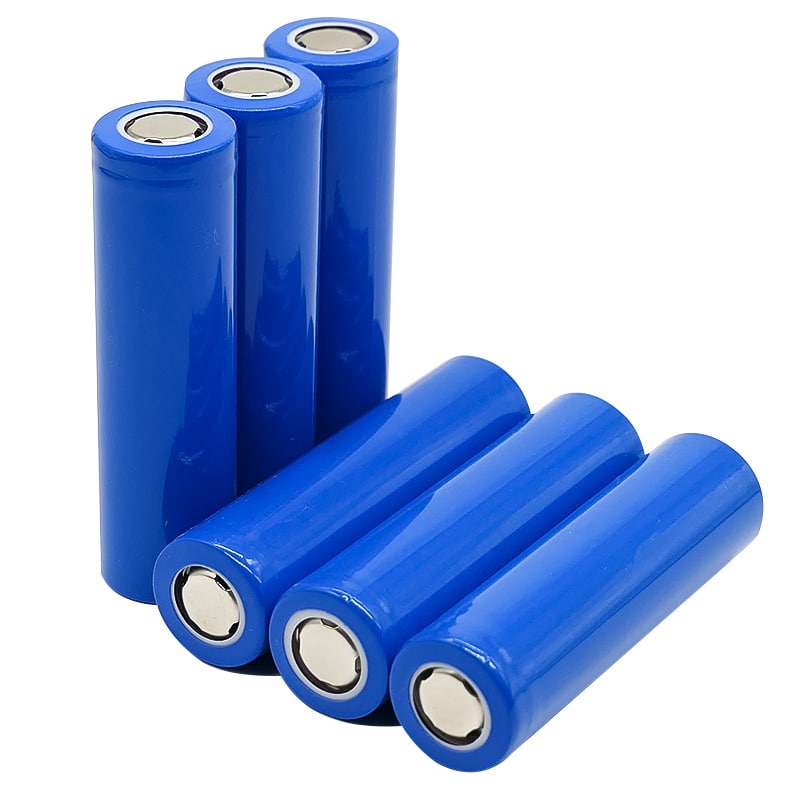

Advantages of lithium-ion batteries:
1. Ultra long lifespan, lithium-ion batteries can have a cycle life of over 2000 cycles and a service life of 7-8 years, much higher than long-lived lead-acid secondary batteries.
2. High temperature resistance, for example, the electric heating peak value of Lithium iron phosphate battery reaches 350 ℃ -500 ℃.
3. The working voltage is high, and the working voltage of a single battery can reach as high as 3.7-3.8V.
4. No memory effect, the battery can be charged and used at any time regardless of its state, without the need to be discharged before charging.
Lithium ion batteries have been widely used in portable appliances such as laptops, cameras, and mobile communication due to their unique performance advantages. The developed high-capacity lithium-ion batteries have started trial use in electric vehicles and are expected to become one of the main power sources for electric vehicles in the 21st century, and will be applied in side satellites, aerospace, and energy storage. With the shortage of energy and the pressure of environmental protection in the world. Lithium battery is widely used in the electric vehicle industry, especially the emergence of Lithium iron phosphate material battery, which further promotes the development and application of lithium battery industry.