how do lithium sulfur batteries work
Lithium-sulfur batteries work by utilizing the chemical reactions between lithium and sulfur to generate electrical energy.
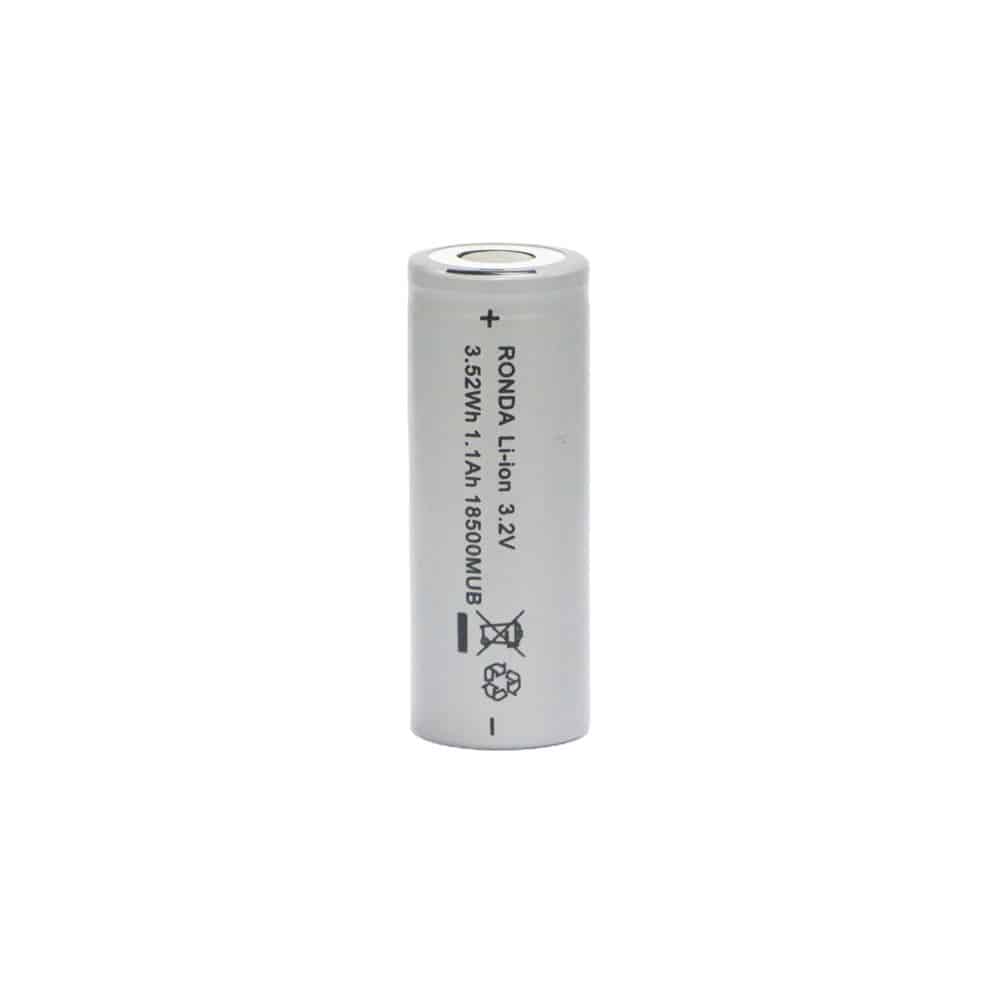

The battery has a cathode made of sulfur and an anode made of lithium. During the discharge process, lithium ions move from the anode to the cathode, while electrons flow through an external circuit to power a device or system.
At the same time, sulfur molecules react with lithium ions and electrons to form compounds such as lithium sulfide (Li2S) and lithium polysulfides (Li2Sx), releasing energy in the process.
During charging, the opposite reaction occurs, with lithium ions moving back to the anode and sulfur being re-deposited on the cathode.
One of the advantages of lithium-sulfur batteries is their high theoretical energy density, which means they can potentially store more energy than other types of batteries. However, they are still being developed and face challenges such as limited cycle life and low power output.